Mr. Haycock,
I consider myself well versed on steroids and how they work, but one thing that continually has me puzzled is this; if there is only one androgen receptor that all steroids bind to in order to induce growth, how come there are so many diverse effects of different synthetic steroids. Some make you bloat, others don’t. Some give you insomnia, other don’t. Some give you hiccups and make you snore, while yet again, others don’t. No one has been able to offer me an explanation for this. Any insight you might shed on this would be really appreciated.
Thanks in advance.
Answer:Much of the confusion about the wide range of side effects of steroids comes from their various non-genomic actions. As the term “non-genomic” doesn’t seem to come up very often in locker room steroid conversations let me explain.
Most people know that there is only one typical, or sometimes called “classical”, androgen receptor (AR). The AR is an intracellular receptor, meaning that it resides within cells (as apposed to the membrane surface) and once bound to an androgen, travels to the nucleus of the cell and binds to the DNA where it initiates the expression of various proteins.
The AR exerts a wide range of effects even though there is only one typical AR. Testosterone (Test) is able to exert different effects in different tissues by virtue of it acting “as is” in some tissues, and acting as its 5-alpha reduced counterpart dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in the same and/or other tissues.
DHT has different binding properties than Test. DHT binds stronger, and stays bound longer than Test. This subtle difference in the strength and duration of binding is able to produce a tremendous range of different actions in the body from the time you’re a fetus to a full grown adult.
Some synthetic steroids are more like Test, and others are more like DHT. But this still doesn’t explain all the differences seen among synthetic androgens. The differences beyond binding properties can then be explained by these “non-genomic” properties mentioned earlier.
Within the last 5 years or so, more attention has been drawn to the non-genomic effects of steroids and trying to understand them. They are called “non-genomic” because they don’t directly involve the steroid bound to the AR acting directly on the cells DNA.
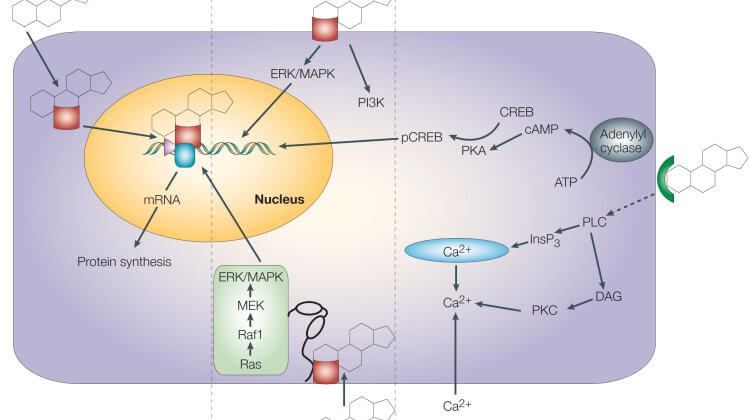
It is now understood that steroids can act on the cell membrane to bring about various second messenger effects. These second messenger pathways involve kinase pathways driven by classical receptors (MAPk, ERK, MEK, etc), as well as cyclic AMP, lipase and other kinase pathways (PI3K, PKA, PKC, etc), including ion fluxes (Ca++), which are driven by atypical receptors. All in all, steroids affect cells through several different pathways and at least one atypical steroid receptor, none of which involve what most people consider the true “intracellular” mechanism of steroid action.
Most all of these non-genomic affects of steroids are acute, or immediate. Meaning, they occur within seconds or minutes of the steroid interacting with the cell. This helps to explain why so many different organs have androgen receptors or are sensitive to androgen levels. For example, in tissues taken from rats, (in order of sensitivity):
- Hypothalamus
- Adrenal gland
- Epididymis
- Thyroid gland
- Pituitary gland
- Quadriceps muscle
- Kidney
- Seminal vesicle
- Testis
- Liver
- Submaxillary gland
- Bulbocavernosus muscle (penis)
- Vagina
- Heart
- Ovary
- Uterus
The hypothalamus, part of the CNS, has a higher concentration of ARs than even the quads. That is an interesting fact. Of course this is from rats but humans would no doubt show more or less “similar” distributions.
One question that has recently been brought to my attention deals with how steroids increase strength. Aside from increases in contractile proteins, strength is largely a product of the nervous system. The involvement of the nervous system in generating strength starts in the brain (which can show fatigue believe it or not) and finishes with the structures involved in excitation contraction coupling.
It is perfectly reasonable that androgens act as a direct CNS stimulant through non-genomic pathways by increasing cAMP activity and enhancing Ca++ flux from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Keep in mind that these are the same second messenger pathways utilized by catecholamines and like drugs including adrenaline, noradrenaline, ephedrine, and caffeine.
It is time for bodybuilders and steroid gurus alike to update their knowledge of the mechanism of action of the drugs the use and direct the use of. There is plenty of research available (see below) so no one claiming to be an expert has an excuse not to be well informed about the non-genomic actions of steroids.
Sample References: (There are many, many, more like these)
1. Losel R, Wehling M. Nongenomic actions of steroid hormones. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jan;4(1):46-55.
2: Schmidt BM, Christ M, Falkenstein E, Wehling M. Nongenomic steroid actions: completing the puzzle. Aldosterone as an example. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 1998;106(6):441-5.
3: Cato AC, Nestl A, Mink S. Rapid actions of steroid receptors in cellular signaling pathways. Sci STKE. 2002 Jun 25;2002(138):RE9.
4: Christ M, Haseroth K, Falkenstein E, Wehling M. Nongenomic steroid actions: fact or fantasy? Vitam Horm. 1999;57:325-73.
5: Falkenstein E, Tillmann HC, Christ M, Feuring M, Wehling M. Multiple actions of steroid hormones–a focus on rapid, nongenomic effects. Pharmacol Rev. 2000 Dec;52(4):513-56.
6: Wehling M. Specific, nongenomic actions of steroid hormones. Annu Rev Physiol. 1997;59:365-93.
7: Schmidt BM, Gerdes D, Feuring M, Falkenstein E, Christ M, Wehling M. Rapid, nongenomic steroid actions: A new age? Front Neuroendocrinol. 2000 Jan;21(1):57-94.
8: Gerdes D, Christ M, Haseroth K, Notzon A, Falkenstein E, Wehling M. Nongenomic actions of steroids–from the laboratory to clinical implications. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2000 Jul-Aug;13(7):853-78.
9: Joels M. Modulatory actions of steroid hormones and neuropeptides on electrical activity in brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 Sep 29;405(1-3):207-16.
10: Spindler KD. Interactions between steroid hormones and the nervous system. Neurotoxicology. 1997;18(3):745-54.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.