cvictorg
New Member
Can Exercise Keep You Young? - NYTimes.com
Endurance exercise rescues progeroid aging and induces systemic mitochondrial rejuvenation in mtDNA mutator mice — PNAS
Indeed, in heartening new research published last week in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, exercise reduced or eliminated almost every detrimental effect of aging in mice that had been genetically programmed to grow old at an accelerated pace.
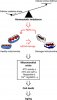
In the experiment, Dr. Tarnopolsky and his colleagues used lab rodents that carry a genetic mutation affecting how well their bodies repair malfunctioning mitochondria, which are tiny organelles within cells. Mitochondria combine oxygen and nutrients to create fuel for the cells — they are microscopic power generators.
The mice that Dr. Tarnopolsky and his colleagues used lacked the primary mitochondrial repair mechanism, so they developed malfunctioning mitochondria early in their lives, as early as 3 months of age, the human equivalent of age 20. By the time they reached 8 months, or their early 60s in human terms, the animals were extremely frail and decrepit, with spindly muscles, shrunken brains, enlarged hearts, shriveled gonads and patchy, graying fur. Listless, they barely moved around their cages. All were dead before reaching a year of age.
Except the mice that exercised.
Half of the mice were allowed to run on a wheel for 45 minutes three times a week, beginning at 3 months. These rodent runners were required to maintain a fairly brisk pace, Dr. Tarnopolsky said: “It was about like a person running a 50- or 55-minute 10K.” (A 10K race is 6.2 miles.) The mice continued this regimen for five months.
At 8 months, when their sedentary lab mates were bald, frail and dying, the running rats remained youthful. They had full pelts of dark fur, no salt-and-pepper shadings. They also had maintained almost all of their muscle mass and brain volume. Their gonads were normal, as were their hearts. They could balance on narrow rods, the showoffs.
But perhaps most remarkable, although they still harbored the mutation that should have affected mitochondrial repair, they had more mitochondria over all and far fewer with mutations than the sedentary mice had. At 1 year, none of the exercising mice had died of natural causes. (Some were sacrificed to compare their cellular health to that of the unexercised mice, all of whom were, by that age, dead.)
Endurance exercise rescues progeroid aging and induces systemic mitochondrial rejuvenation in mtDNA mutator mice — PNAS
Indeed, in heartening new research published last week in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, exercise reduced or eliminated almost every detrimental effect of aging in mice that had been genetically programmed to grow old at an accelerated pace.
In the experiment, Dr. Tarnopolsky and his colleagues used lab rodents that carry a genetic mutation affecting how well their bodies repair malfunctioning mitochondria, which are tiny organelles within cells. Mitochondria combine oxygen and nutrients to create fuel for the cells — they are microscopic power generators.
The mice that Dr. Tarnopolsky and his colleagues used lacked the primary mitochondrial repair mechanism, so they developed malfunctioning mitochondria early in their lives, as early as 3 months of age, the human equivalent of age 20. By the time they reached 8 months, or their early 60s in human terms, the animals were extremely frail and decrepit, with spindly muscles, shrunken brains, enlarged hearts, shriveled gonads and patchy, graying fur. Listless, they barely moved around their cages. All were dead before reaching a year of age.
Except the mice that exercised.
Half of the mice were allowed to run on a wheel for 45 minutes three times a week, beginning at 3 months. These rodent runners were required to maintain a fairly brisk pace, Dr. Tarnopolsky said: “It was about like a person running a 50- or 55-minute 10K.” (A 10K race is 6.2 miles.) The mice continued this regimen for five months.
At 8 months, when their sedentary lab mates were bald, frail and dying, the running rats remained youthful. They had full pelts of dark fur, no salt-and-pepper shadings. They also had maintained almost all of their muscle mass and brain volume. Their gonads were normal, as were their hearts. They could balance on narrow rods, the showoffs.
But perhaps most remarkable, although they still harbored the mutation that should have affected mitochondrial repair, they had more mitochondria over all and far fewer with mutations than the sedentary mice had. At 1 year, none of the exercising mice had died of natural causes. (Some were sacrificed to compare their cellular health to that of the unexercised mice, all of whom were, by that age, dead.)