New to these forums. I am thinking about starting a 10 week cycle of Test E
Weeks 1-10 Test E, 500mg (250mg twice a week)
Week 11 Off
Week 12 PCT
I am unsure about which PCT I should take. Clomid, Nolvadex, or Arimidex. I have heard to take Nolva and Clomid Post cycle. Should I take Arimidex during the cycle of just leave it out of the equation? I want to reduce the risk of gyno but I hear that some estrogen is good for your mass building.
Also, should I add some deca with the Test or just stick with the Test E for my first time?
Is there a risk of hair loss on a cycle like this?
The cycle reminds me of what is now called the classical article definitely demonstrating that anabolic steroids by themselves increase muscle mass and muscle strength. The anabolic steroid used was testosterone cypionate alone (600 mg/week). The trial length was 10 weeks! Since this is so close to what you plan on using, I thought you might want to familiarize yourself with the article details (download).
There are many things to discuss, but I wish to only point out one in an early post for this thread. That is the suggestion for when to begin PCT. It is not too wise to begin 2 weeks after the last injection. Testosterone enanthate (half-life 10-14 days) will accumulate more than cypionate (half-life 7-10 days) leading to a serum testosterone level around 7,000-10,000 ng/dL. The level of testosterone in the study a 1 week after the last injection was around 3,000 ng/dL. At these levels, PCT needs to be more carefully planned.
Bhasin S, Storer TW, Berman N, et al.
The Effects of Supraphysiologic Doses of Testosterone on Muscle Size and Strength in Normal Men. N Engl J Med 1996;335(1):1-7.
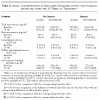
Background Athletes often take androgenic steroids in an attempt to increase their strength. The efficacy of these substances for this purpose is unsubstantiated, however. Methods We randomly assigned 43 normal men to one of four groups: placebo with no exercise, testosterone with no exercise, placebo plus exercise, and testosterone plus exercise.
The men received injections of 600 mg of testosterone enanthate or placebo weekly for 10 weeks. The men in the exercise groups performed standardized weight-lifting exercises three times weekly. Before and after the treatment period, fat-free mass was determined by underwater weighing, muscle size was measured by magnetic resonance imaging, and the strength of the arms and legs was assessed by bench-press and squatting exercises, respectively. Results Among the men in the no-exercise groups, those given testosterone had greater increases than those given placebo in muscle size in their arms (mean [{+/-}SE] change in triceps area, 424{+/-}104 vs. -81{+/-}109 mm2; P<0.05) and legs (change in quadriceps area, 607{+/-}123 vs. -131{+/-}111 mm2; P<0.05) and greater increases in strength in the bench-press (9{+/-}4 vs. -1{+/-}1 kg, P<0.05) and squatting exercises (16{+/-}4 vs. 3{+/-}1 kg, P<0.05). The men assigned to testosterone and exercise had greater increases in fat-free mass (6.1{+/-}0.6 kg) and muscle size (triceps area, 501{+/-}104 mm2; quadriceps area, 1174{+/-}91 mm2) than those assigned to either no-exercise group, and greater increases in muscle strength (bench-press strength, 22{+/-}2 kg; squatting-exercise capacity, 38{+/-}4 kg) than either no-exercise group. Neither mood nor behavior was altered in any group. Conclusions Supraphysiologic doses of testosterone, especially when combined with strength training, increase fat-free mass and muscle size and strength in normal men.