Robinson EC, Roy D, Driver BE. Deflate to Extricate: A Technique for Rectal Foreign Body Removal of Inflatable Ball. The Journal of emergency medicine 2017. http://www.jem-journal.com/article/S0736-4679(17)30992-7/abstract
BACKGROUND: Rectal foreign bodies are commonly encountered in the emergency department (ED). Three techniques are well described in literature, including using a Foley catheter, "scooping" the object out, or grasping the object directly with ring forceps. We present a novel extraction method for an inflatable foreign body.
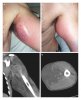
CASE REPORT: A 27-year-old man presented to the ED 13 h after inserting a rubber inflatable child's ball into his rectum. After well-described extraction techniques failed to remove the ball, an 18-gauge needle at the end of a syringe was inserted into the rectum to puncture the ball and partially deflate it. The ball was then able to be removed easily.
WHY SHOULD AN EMERGENCY PHYSICIAN BE AWARE OF THIS?: Although recent published literature has pushed for early consultation of surgical specialties in lieu of emergency physician bedside extraction, this case report highlights the ability of emergency physicians to modify known extraction techniques to safely remove rectal foreign bodies in well-appearing patients at the bedside using appropriate analgesia, positioning, and readily available equipment.
BACKGROUND: Rectal foreign bodies are commonly encountered in the emergency department (ED). Three techniques are well described in literature, including using a Foley catheter, "scooping" the object out, or grasping the object directly with ring forceps. We present a novel extraction method for an inflatable foreign body.
CASE REPORT: A 27-year-old man presented to the ED 13 h after inserting a rubber inflatable child's ball into his rectum. After well-described extraction techniques failed to remove the ball, an 18-gauge needle at the end of a syringe was inserted into the rectum to puncture the ball and partially deflate it. The ball was then able to be removed easily.
WHY SHOULD AN EMERGENCY PHYSICIAN BE AWARE OF THIS?: Although recent published literature has pushed for early consultation of surgical specialties in lieu of emergency physician bedside extraction, this case report highlights the ability of emergency physicians to modify known extraction techniques to safely remove rectal foreign bodies in well-appearing patients at the bedside using appropriate analgesia, positioning, and readily available equipment.