bananafeet
Member
Thought I'd start this thread to cover testosterone and ALL it's downstream metabolites and their actions.
No AI slop. I hate that shit. All this is from textbooks.
Testosterone is derived from cholesterol by various reducing processes by the Leydig cells in the testies (and ovaries):
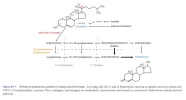
Source: [1]
This process is regulated by the HPTA:
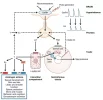
Source: [2]
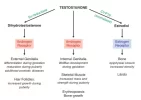
After entering circulation it is turned into paracrine and exocrine metabolites and hormones, although a large amount of estrodial and DHT are converted locally in the testies:
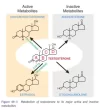
Source: [1]
During the development of the fetus, and through puberty testosterone and it's metabolite DHT are responsible for the virilisation process. Estrogen is responsible for closing the growth plates in the long bones ending the increase in height during puberty. HCG produced by the mother stimulates the testies in the foetus to produce testosterone and start the sex differentiation process.
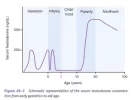
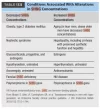
Most of the testosterone is bound to either albumin or SHBG. Between 97% and 99% of circulating T and E2 is reversibly bound to SHBG (Source [2]). Testosterone and E2 which is bound to SHBG can not act on tissues. The reduction in free testosterone due to a drop in total testosterone and a simultaneous increase in SHBG effectively reduces the bioavailabilty of testosterone. SHBG levels can be influenced by several factors:
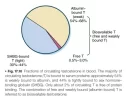
Source: [1]
Estradiol and DHT have many downstream metabolites. These metabolites have many downstream effects:
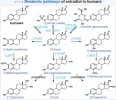
Source: Estradiol - Wikipedia
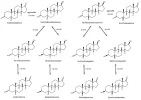
Source: Dihydrotestosterone - Wikipedia
It's interesting that the same enzyme 3aHSD that makes DHT non-anabolic in muscle tissue is the same enyzme that produces the neurosteroid metabolites.
P.S Well that's prettry much all the low hanging fruit gone. Info is getting harder to find. I'll keep looking. Feel free to add anything else related to neurosteroids or testosterone's downstream effects. Obviously estrodial will be easy. But the DHT metabolites aren't studied a lot. Allopregnanolone is implicated in female mood disorders and is studied quite a bit. I might find some data there.
Source [1] Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 14th Edition
Source [2] WILLIAMS TEXTBOOK OF ENDOCRINOLOGY , FIFTEENTH EDITION
Source [3] Matthiesson KL, Stanton PG, O’Donnell L, et al. Effects of testosterone and levonorgestrel combined with a 5alpha-reductase inhibitor or gonadotropin releasing hormone antagonist on spermatogenesis and intratesticular steroid levels in normal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(10):5647–5655.
Source [4] Thigpen AE, Silver RI, Guileyardo JM, Casey ML, McConnell JD, Russell DW. Tissue distribution and ontogeny of steroid 5 alpha reductase isozyme expression. J Clin Invest. 1993;92(2):903–910.
Source [5] Horton R. Sex steroid production and secretion in the male. Andrologia. 1978;10(3):183–194.
No AI slop. I hate that shit. All this is from textbooks.
Testosterone is derived from cholesterol by various reducing processes by the Leydig cells in the testies (and ovaries):

Source: [1]
This process is regulated by the HPTA:

Source: [2]
After entering circulation it is turned into paracrine and exocrine metabolites and hormones, although a large amount of estrodial and DHT are converted locally in the testies:
Source: [3]Intratesticular testosterone is converted within the testes to its active metabolites, estradiol and DHT, by P450 19A1(aromatase) and 5α-reductase (SRD5A1), respectively. As with testosterone, intratesticular concentrations of estradiol are about 100-fold higher than serum estradiol concentrations; however, intratesticular concentrations of DHT are only approximately 15-fold higher than concentrations in the circulation.

Source: [1]
During the development of the fetus, and through puberty testosterone and it's metabolite DHT are responsible for the virilisation process. Estrogen is responsible for closing the growth plates in the long bones ending the increase in height during puberty. HCG produced by the mother stimulates the testies in the foetus to produce testosterone and start the sex differentiation process.


Testosterone is converted to DHT, an androgen that is 2.5 to 3.0 times more potent than testosterone, by SRD5A1 and SRD5A2. These two isoenzymes of 5α-reductase differ in the optimal pH for their activity and in their expression patterns.
Source [4]Many of the biologic actions of testosterone are mediated by these active metabolites, acting through mechanisms that are dependent on ERα and ERβ (estradiol) or on AR (DHT). These active metabolites are formed and act locally as paracrine or autocrine regulators, and they also are secreted and act as endocrine regulators of target tissue function.
Source [5]Approximately 15% to 25% of circulating estradiol is produced by the testes, primarily by Leydig cells.
Source [2]SRD5A2 is expressed most highly in prostate, epididymis, seminal vesicles, genital skin, and liver and at lower concentrations in other tissues, such as certain
brain regions, non-genital skin, testis, and kidney. SRD5A1 is expressed most highly in non-genital skin (hair follicles), liver, and certain brain regions and at lower concentrations in prostate, epididymis, seminal vesicles, genital skin, testis, adrenal, and kidney.
Approximately 200 to 300 μg of DHT is produced daily, mostly from 5α-reduction of testosterone in peripheral tissues (predominantly skin and liver). The prostate and testis contribute relatively little to concentrations of DHT in blood.
Most of the testosterone is bound to either albumin or SHBG. Between 97% and 99% of circulating T and E2 is reversibly bound to SHBG (Source [2]). Testosterone and E2 which is bound to SHBG can not act on tissues. The reduction in free testosterone due to a drop in total testosterone and a simultaneous increase in SHBG effectively reduces the bioavailabilty of testosterone. SHBG levels can be influenced by several factors:


Source: [1]
Estradiol and DHT have many downstream metabolites. These metabolites have many downstream effects:

Source: Estradiol - Wikipedia

Source: Dihydrotestosterone - Wikipedia
It's interesting that the same enzyme 3aHSD that makes DHT non-anabolic in muscle tissue is the same enyzme that produces the neurosteroid metabolites.
Source: 3α-Androstanediol - WikipediaAs a neurosteroid, it acts as a potent positive allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor, and has been found to have rewarding, anxiolytic, pro-sexual, and anticonvulsant effects. As androgens such as testosterone and DHT are known to have many of the same effects as 3α-diol and are converted into it in vivo, it is thought that this compound may in part be responsible for said effects.
P.S Well that's prettry much all the low hanging fruit gone. Info is getting harder to find. I'll keep looking. Feel free to add anything else related to neurosteroids or testosterone's downstream effects. Obviously estrodial will be easy. But the DHT metabolites aren't studied a lot. Allopregnanolone is implicated in female mood disorders and is studied quite a bit. I might find some data there.
Source [1] Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 14th Edition
Source [2] WILLIAMS TEXTBOOK OF ENDOCRINOLOGY , FIFTEENTH EDITION
Source [3] Matthiesson KL, Stanton PG, O’Donnell L, et al. Effects of testosterone and levonorgestrel combined with a 5alpha-reductase inhibitor or gonadotropin releasing hormone antagonist on spermatogenesis and intratesticular steroid levels in normal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(10):5647–5655.
Source [4] Thigpen AE, Silver RI, Guileyardo JM, Casey ML, McConnell JD, Russell DW. Tissue distribution and ontogeny of steroid 5 alpha reductase isozyme expression. J Clin Invest. 1993;92(2):903–910.
Source [5] Horton R. Sex steroid production and secretion in the male. Andrologia. 1978;10(3):183–194.

