Some products never advertised in my list, few kits in stock:
BPC157 2 mg:$30/kit (3 kits left)
Sermorelin 5mg: $78/kit (1 kit left)
Humanin 2mg:$118/kit (3 kits left)
Mots-C 25mg: $220/kit (1 kit left)
CJC no Dac 5mg: $80/kit (8 kits left)
TB500 2mg: $45/kit (10 kits left)
Benefits Of Humanin
1. Improves Mitochondrial Function
Humaninin (HN) directly inhibits oxidative stress on the mitochondrial membrane, thus protecting mitochondria from dying.
R
HN inhibits
Cytochrome C release from mitochondria and can increase their production of energy (ATP).
HN improves mitochondrial levels of
Glutathione (GSH) as well.
R
HN can also prevent
Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-like episodes (MELAS) by directly increasing cellular ATP levels in lymphocytes.
Humanin also induces
Mitochondrial Biogenesis (growth of new mitochondria).
2. Protects Cells From Dying
HN can also protect cells from oxidative stress.
HN improves cell survival by binding to and inhibiting by
Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 (IGFBP-3) and
Bcl2-Associated X protein (Bax).
HN can also promote cell survival by binding to and deactivating proapoptotic BH3 proteins
Truncated Form of Bid (tBid) and
Extra Long Isoform of Bim (BimEL).
3. May Enhance Longevity
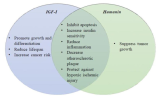
View attachment 251325
Growth Hormone (GH) negatively regulates HN levels.
R
For example, mice that were unable to produce adequate amounts of GH had higher amounts of HN and lived longer than normal mice.
R
Children of centenarians have 3x higher levels of HN than controls.
R
HN can act as a
Calorie-Restriction Mimetic (CRM) by suppressing
Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) levels.
R
HN has very similar actions to IGF-1 (see section above):
R
- Activate ERK1/2
- Activate JAK2-STAT3
- Activate PI3K/Akt (helps with stroke)
- Cardioprotective
- Controls cell death, metabolism, and transcription
- Degrading Atherosclerotic Plaques
- Enhance Brain Aβ Clearance
- Enhancing Insulin Sensitivity
- Found in Mitochondria, plasma, cells, skeletal muscle, liver, fat, and hypothalamus
- Lowering Inflammation
- Inhibiting Cell death
- Suppressing Hypoxia
Although, HN and IGF-1 do have opposite effects on longevity and cancer growth, and both show a decline in expression with aging.
R
For example, HN protects against cell senescence (biological aging of a cell).
R
4. Ameliorates Alzehiemer's Disease And Improves Short-Term Memory
HN can protect brain cells against
Amyloid-Beta (AB)-induced cell death and increase clearance AB levels, a common pathology seen
Alzheimer's Disease (AD).
R R R
HN can also protect the brain against
Tau Hyperphosphorylation (a pathology of AD).
R
For example, HN can protect against
Okadaic Acid (OA), a toxin extracted from marine life that causes tau hyperphosphorylation.
R
HN may improve memory.
For example, HN can also reverse
Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) loss from AB, in important mechanism used to form memory.
R
HN can also prevent memory loss from other
Anticholinergic drugs.
R
For example, scopolamine, a
Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor (mAChR) antagonist, can cause short-term memory loss and is a standard in testing AD animal models.
R
A modified version of HN called
Humanin G (HNG) can reverse the short-term memory loss from scopolamine.
R
This modification (HNG) has shown to increase the neuroprotective effects of HN by 1000-fold.
R
HNG taken intranasally can reduces AB accumulation and ameliorates memory deficit in AD animal models.
R
HN may protect against
Insulin Resistance (IR) in the brain, a main pathology of Type 3 Alzheimer's/Diabetes.
R R
For example, by stimulating
STAT3 and inhibiting
IGFBP3 in the hypothalamus, HN is a powerful insulin sensitizer and may help with IR in AD.
R R R
In the hippocampus, HNG can improve
Autophagy by regulating
IRS-1/mTOR signaling.
R
HN also provides neuroprotection against some
Familial Alzheimer's Disease (FAD) genes including presenilin 1, presenilin 2, and mutated
Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP).
R R
HN also binds to the receptor for
Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor (CNTF), which is an important for neurodegenerative diseases, spinal cord injuries, retinal degeneration, autoimmune neuroinflammation and obesity-related metabolic diseases.
R
5. Combats Proteopathy, Neuroinflammation, And Excitotoxicity
In the
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), ROS causes a calcium efflux leading to
Proteopathy (toxic unfolded/misfolded protein aggregates).
R
HN protects against proteopathy in 2 ways:
- HN can inhibit ROS formation R
- HN can inhibit calcium release in the ER R
For example, HN can protect against prion-proteopathy.
R
HN also protects against
Lipopolysaccharide-induced (
Endotoxemia) neuroinflammation.
R
HN also protects against
excitotoxicity (both via action on NMDARs and independently).
R
For example, HN can prevent
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and
Nitric Oxide (NO) induced excitotoxicity caused by the overactivation of the NMDA receptors.
R
HN can also reduce
Lactate-Dehydrogenase (LDH) in the brain.
R
6. Protects Against Insulin Resistance
HN can inhibit pancreatic beta-cell death and improve
Glucose tolerance in non-obese diabetic (NOD) animal models.
R
This may be beneficial for both
Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) and
Type 2 Diabetes (T2D).
R R
By acting on the hypothalamus, HN can also increase
Insulin sensitivity in the liver and stabilize blood glucose levels.
R
HN may be a good biomarker for fasting glucose-related oxidative stress.
R
HNG acutely increases
Triglyceride (TG) secretion from the liver.
R
7. Combats Obesity And Weight Gain
HN can prevent weight gain by increasing glucose stimulated insulin release and decreasing body
Weight Gain and visceral fat.
R R
8. Protects The Eyes
Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) is caused degeneration of the retina from oxidative stress resulting in irreversible vision loss.
R
The ER of mitochondria play a huge role in protecting the
Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) in AMD.
R
HN and HNG both prevent AMD as it can protect against oxidative stress and cell death of the RPE and ER by increasing mitochondrial GSH levels and reducing ROS,
Caspase 3 and
Caspase 4 levels.
R R
9. May Fight Spinocerebellar Ataxia And Huntington's Disease
Spinocerebellar Ataxia (SA) and
Huntington's Disease (HD) are characterized by
Polyglutamine (PolyQ) toxicity.
R
HN can prevent PolyQ-induced mitochondrial dysfunction.
R
10. May Help With Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
HN may help Familial
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS).
For example, animal models with mutations in G93A-SOD1, HN dose-dependently improved motor performance and prolonged survival of ALS mice.
R
11. May Protect Against Sunburn
HN can protect against
Ultraviolet (UV)-induced cell death.
R
12. Protects The Vascular System
HN levels have been shown to be high in patients with atherosclerotic plaques and may protect against atherosclerosis.
R
For example, in animal models that were unable to express
APOE (an important protein for cholesterol metabolism), HNG was able to improve cardiovascular function from a high cholesterol diet (reducing plaque ~90%).
R
HN can protect HN cells from cells from oxidative stress induced by
Oxidized LDL (oxLDL).
R R
By increasing
AMPK and
eNOS, during a heart attack HNG can protect against damage induced by left coronary occlusion, reducing infarct size and oxidative stress.
R
13. Protects Against Hypoxia And Ischemia
HN can attenuate the stresses caused by
hypoxia and
ischemia.
By activating
PI3K/
Akt and
Jak2/
Stat3, HNG is neuroprotective during hypoxia.
R R
For example, HN can protect against cellular hypoxia induced by
Compound Cobalt Chloride (CoCl₂).
R
Cuprizone (CPZ), a copper chelator, provokes demyelination and schizophrenia-like symptoms.
R
HN can suppress neuroinflammation and cognitive deficits from CPZ use.
R
HN has shown to induce axonal remyelination in hypoxic brains.
R
A major problem from
ischemia is loss of blood flow which results in the reduction of growth factors, and thus cell death.
HN can prevent cell death from ischemia and improve hypoxic cell's ability to create energy (ATP).
R R
HN may also be beneficial in a
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI), as HN can protect against ischemic and
hemorrhagic stroke-induced damage.
R R
For example, in animal models, HNG was able to reduce infarct volume size by 50%.
R
One reason why HNG may protect against TBI is by upregulation of
Suppressor Of Cytokine Signaling 3 (SOCS3).
R
14. Protects The Colon
In experimental models of
Ulcerative Colitis (UC), HNG can protect against inflammation in the colon and ameliorate weight loss.
R
15. Protects The Kidneys From Inflammation
HN can protect the kidneys from inflammation.
R
For example, in
APOE deficient mice, HN was able to protect against the development of kidney disease.
R
16. Protects Male Reproductive System
HN is present at all stages of testicle development.
R
HN can protect against testicular and sperm cells from death.
R R