Hey guys!
New week, new long article! I will start publishing medium and short articles, if you guys are interested on a certain topic, you are more than welcome to ask me for it.
In this article I am going to talk about the pulse pressure, which is for me one of the main indicators of the health of an individual. Nowadays more and more bodybuilders suffer from health problems that could be easily identified and alleviated by a correct measurement of pulse pressure, in this article we are going to teach you how to measure pulse pressure, to obtain information based on your values to know when to seek professional help, and a few tips to keep it in the healthiest range possible.
Introduction
Pulse pressure is an indicator of the stiffness or flexibility of the arteries and how well the heart is pumping blood.
The heart contracts and relaxes rhythmically, expelling blood and allowing new blood to enter. The contraction of the heart is known as systole, while its relaxation is known as diastole.
Therefore, systolic blood pressure is the pressure that exists in the arteries when the heart contracts, and diastolic blood pressure is the pressure that exists in the arteries when the heart relaxes, so when we go to the doctor to have them measure us voltage give us two numbers, for example 120/70.
Pulse pressure is the difference between systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure, therefore: pulse pressure = systolic blood pressure - diastolic blood pressure.
Basically, pulse pressure measures the force the heart generates each time it contracts, being an indicator of how well the heart is pumping blood and the flexibility of the arteries.
How to calculate pulse pressure.
Pulse pressure = systolic blood pressure - diastolic blood pressure.
Therefore, if the doctor tells us that we have a blood pressure of 120/70 mmHg:
120-70= 50 which will be our pulse pressure
The healthy range for pulse pressure is 40 to 60 mmHg.
How to interpret the results
There are three types of results, a low pulse pressure (less than 40mmHg), a normal pulse pressure (40-60mmHg) and a high pulse pressure (greater than 60mmHg), depending on the result we may have some health problems or others, or also be completely healthy.
Low pulse pressure
Low pulse pressure is anything that is less than 40mmHg, this is an indicator that the heart is not pumping an adequate amount of blood.
It mainly has three causes:
Significant blood loss
This is the easiest cause to diagnose, significant blood loss will cause the heart to be unable to pump enough blood.
Chronic heart failure
In the most advanced cases of chronic heart failure, a loss of pulse pressure can be seen, which means that at the beginning of the disease, a notable decrease cannot be seen.
Aortic stenosis
In aortic stenosis, the aortic valve narrows, preventing the necessary amount of blood from being pumped into the aortic artery, causing a significant decrease in systolic blood pressure and therefore a reduction in pulse pressure.
Steroids play an important role here, so it is a fact to take into account when measuring our blood pressure.
Increased mortality in people with low pulse pressure.
● In the case of stroke patients, 85% of people with low pulse pressure developed disability compared to people with normal pulse pressure.
● In the case of patients with heart failure in the middle and advanced stages, we can find quite interesting data, the most striking being that in a clinical trial in people with advanced heart failure, 84% of the people who died in a two-year period had a low pulse pressure, less than 30mmHg.
Normal pulse pressure
A pulse pressure between 40-60 mmHg is considered normal, pulse pressure tends to increase with age as the arteries harden, so it is in our best interest to maintain a normal pulse pressure for as long as possible.
High pulse pressure
A high pulse pressure is anything higher than 60mmHg, it is usually a good indicator of arterial stiffness (we will focus on this later).
A very important point must be taken into account, the higher the systolic pressure in a person with high pulse pressure, the worse their diagnosis and the greater the risk of suffering from diseases or health problems.
It mainly has 5 causes:
Arteriosclerosis
Hardening of the arteries or arteriosclerosis is the main cause of high pulse pressure, two of the main causes are the accumulation of calcium deposits and fatty plaques, in fact these two are two of the main problems that cause death in bodybuilders, having a much higher risk than the normal population, another reason for the increase in hardening of the arteries is the loss of elastin with age.
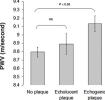
PWV To Vascular calcification
Anemia
Interestingly, anemia can cause high pulse pressure through a very interesting mechanism, the lack of general oxygenation causes an increase in heart rate, thus increasing systolic blood pressure, in order to oxygenate the body, if we remember what I said before, a elevated systolic blood pressure together with elevated pulse pressure is more dangerous, luckily this is a problem that bodybuilders do not usually have.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism (which, for example, can be caused by the abuse of thyroid hormones) can reduce diastolic pressure, increasing pulse pressure.
 Aortic valve regurgitation
Aortic valve regurgitation
This is one of the most dangerous causes of high pulse pressure, and it is typical among bodybuilders since the abuse of PEDs can cause structural remodeling of the heart.
When the aortic valve does not close completely, blood tends to flow back toward the heart, increasing systolic blood pressure and lowering diastolic blood pressure, causing a marked increase in pulse pressure.
Hypogonadism
Fortunately, this cause will not affect most of the people who read this article, a low amount of testosterone increases arterial stiffness, also, although it is not completely proven, it could directly influence a high systolic blood pressure and a lower diastolic blood pressure , increasing pulse pressure.
Increased mortality and illnesses in people with high pulse pressure.
Death
A high pulse pressure increases the chance of dying from heart disease and all its causes, regardless of other factors.
As can be seen in several clinical trials, every 10mmHg increase in pulse pressure increases mortality by 16 to 20%.
In fact, in the population over 65 years of age, it can be considered a better indicator of mortality than blood pressure.
Congestive heart failure
A high pulse pressure drastically increases the chances of suffering from congestive heart failure, in fact, as can be seen in a clinical trial, a simple difference of 14mmHg increases the probability of suffering from congestive heart failure by 55%.
Heart attacks
An elevated pulse pressure can increase the chances of heart attacks up to twofold according to a clinical trial, it has also been shown that for every 10mmHg increase in pulse pressure the probability of suffering a repeated heart attack increases by 12%.
Erectile dysfunction
High pulse pressure often leads to increased arterial stiffness, which often leads to erectile dysfunction.
Arrhythmias
High pulse pressure leads to a 26% increased chance of atrial fibrillation, one of the main causes of arrhythmias, for every 20mmHg increase in pulse pressure.
What can we do?
● Use antihypertensive type ARBs when necessary/possible (consult a doctor).
● Use beta-blocker drugs when necessary/possible (consult a doctor).
● Consuming vitamin K, vitamin K helps reduce arterial calcification, preventing calcium from sticking to the arteries, it is also proven that a deficient amount of vitamin K increases pulse pressure.
● Consuming Omega 3 fatty oils reduce arterial fatty plaques and improve pulse pressure, it is advisable to take a patented brand to avoid taking oxidized fatty acids.
● Consume nitrates, nitrates are fantastic for lowering blood pressure (in addition to giving a good pump in the gym).
● Reduce sodium intake, a high sodium intake tends to increase blood pressure and increase arterial stiffness.
● Doing aerobic exercise of low, medium or high intensity reduces the pulse pressure.
● Use of statins to reduce arterial cholesterol plaques.
● Alleviate water retention which increases blood pressure.
● Reduce steroid doses, do not abuse alcohol and avoid smoking tobacco.
TLDR
Pulse pressure is the difference between systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure, therefore: pulse pressure = systolic blood pressure - diastolic blood pressure.
Basically, pulse pressure measures the force the heart generates each time it contracts, being an indicator of how well the heart is pumping blood and the flexibility of the arteries.
Healthy levels are between 40-60mmHg, levels above or below those can be consequence of serious health issues.



